CS501 Assignment 1 Solution and Discussion
-
Advance Computer Architecture (CS501)
Assignment # 01
Fall 2019
Total marks = 20Deadline Date
12th Nov 2019Please carefully read the following instructions before attempting assignment.
RULES FOR MARKING
It should be clear that your assignment would not get any credit if:
The assignment is submitted after the due date.
The submitted assignment does not open or file is corrupt.
Strict action will be taken if submitted solution is copied from any other student or from the internet.You should consult the recommended books to clarify your concepts as handouts are not enough.
You are supposed to submit your assignment in .doc or docx format.
Any other formats like scan images, PDF, zip, rar, ppt and bmp etc will not be accepted.Objective:
Objective of this assignment is to increase the learning capabilities of the students about
• Performance Measurement of a processor
• Performance Comparison of processors
• Classification of Instruction Set Architecture for different machinesNOTE
No assignment will be accepted after the due date via email in any case (whether it is the case of load shedding or internet malfunctioning etc.). Hence refrain from uploading assignment in the last hour of deadline. It is recommended to upload solution file at least two days before its closing date.
If you find any mistake or confusion in assignment (Question statement), please consult with your instructor before the deadline. After the deadline no queries will be entertained in this regard.
For any query, feel free to email at:
[email protected]Questions No 01 10 marks
Suppose we have a program which contains 200 instructions of different types. We want to execute this program on a 500 MHz processor. The ratio of each type of instruction in the program as well as clocks per instruction for each type of instruction is given below:
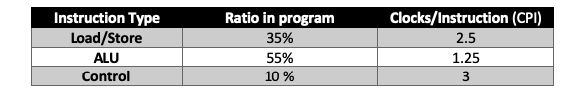
- Calculate the total execution time required by the processor to execute the program.
- If CPI for ALU is decreased by 20% and CPI for Load/Store is increased by 10%, then calculate the execution time.
Questions No 02 10 marks
Write assembly language program for 0-address and 1-address machines to evaluate the following expression.
D = A(B+C) – 2AC/B + C2
Note: A, B, C and D are memory labels.
Good Luck!
-
Solution (A)
The formula to calculate the execution time : Execution Time = IC CPI T
IC for Load / Store Instructions
IC for ALU instructions
IC for Control instructions
= Total Instructions Ratio of Load / Store Instructions = 200 0.35
= 70 instructions
= Total Instructions Ratio of ALU Instructions = 200 0.55
= 110 instructions
= Total Instructions Ratio of Control Instructions = 200 0.10
= 20 instructions
Now, we will calculate the total clock cycles required to execute each type of instructions
Total Clock Cycles for Load / Store
Total Clock Cycles for ALU
Total Clock Cycles for Control
= IC for Load / Store CPI for Load / Store = 70 2.5
= 175 clock cycles
= IC for ALU CPI for ALU = 110 1.25
= 137.5 clock cycles
= IC for control CPI for control = 20 3
= 60 clock cycles
Time required (in seconds) for each clock cycle (T)=1/CPU frequency 1 / 500 106 = 0.002 10−6 seconds
= 210−9 seconds
Now finally, we will calculate the execution time
Execution Time (ET ) = Total Clock Cycles 1/ CPU Frequency
= (175 + 137.5 + 60) (1/ 500 106 ) seconds
= 372.5210−9seconds 1/500106 =210−9seconds = 745 10−9 seconds
= 745 nanosecondsSolution (B)
If decrease the average CPI for ALU by 20%, the new average CPI
New CPI for ALU = 1.25 (100−20)/100 = 1.25 0.8
= 1 CPI
If average CPI for Load / Store instruction is increased by 10%, new average CPI New CPI for Load / Store = 2.5 (100 +10)/100
= 2.5 1.1 = 2.75 CPI
Hence, new execution time will be
ExecutionTime(E.T) = (702.75+1101+203)x(1/500106)seconds
= (192.5+110+60)/(5108)seconds
= 362.5 2 10−9 seconds = 725 10−9 seconds
= 725 nanosecondsQ. 2 Solution:
Solution A (0-Address Code)
PUSH B
PUSH C
ADD ; gives B+C PUSH A
MUL ; gives A(B+C) PUSH 2
PUSH A
MUL ; gives 2A PUSH C
MUL ; gives 2AC
PUSH B
DIV ; gives 2AC/B
SUB ; gives A(B+C) - 2AC/B
PUSH C
PUSH C
MUL ; gives C2
ADD ; gives POP D
A(B+C) - 2AC/B + C2Solution A (1-Address Code)
LDA C MULA C STA X
LDA A MULA C MULA 2
; loads the value stored at memory location C in Accumulator ; gives C2
; stores C2 at memory location X
; loads the value stored at memory location A in Accumulator ; gives AC
; gives 2AC
DIVA B ADDA X STA Y
LDA B ADDA C MULA A SUB Y STA D
; gives 2AC/B
; adding 2AC/B with C2 stored in X gives 2AC/B + C2 ; stores 2AC/B + C2 at memory location Y
; loads the value stored at memory location B in Accumulator ; gives (B+C)
; gives A(B+C)
; subtracts 2AC/B + C2 from A(B+C)
; stores the result at memory location D -
-
Solution (A)
The formula to calculate the execution time : Execution Time = IC CPI T
IC for Load / Store Instructions
IC for ALU instructions
IC for Control instructions
= Total Instructions Ratio of Load / Store Instructions = 200 0.35
= 70 instructions
= Total Instructions Ratio of ALU Instructions = 200 0.55
= 110 instructions
= Total Instructions Ratio of Control Instructions = 200 0.10
= 20 instructions
Now, we will calculate the total clock cycles required to execute each type of instructions
Total Clock Cycles for Load / Store
Total Clock Cycles for ALU
Total Clock Cycles for Control
= IC for Load / Store CPI for Load / Store = 70 2.5
= 175 clock cycles
= IC for ALU CPI for ALU = 110 1.25
= 137.5 clock cycles
= IC for control CPI for control = 20 3
= 60 clock cycles
Time required (in seconds) for each clock cycle (T)=1/CPU frequency 1 / 500 106 = 0.002 10−6 seconds
= 210−9 seconds
Now finally, we will calculate the execution time
Execution Time (ET ) = Total Clock Cycles 1/ CPU Frequency
= (175 + 137.5 + 60) (1/ 500 106 ) seconds
= 372.5210−9seconds 1/500106 =210−9seconds = 745 10−9 seconds
= 745 nanosecondsSolution (B)
If decrease the average CPI for ALU by 20%, the new average CPI
New CPI for ALU = 1.25 (100−20)/100 = 1.25 0.8
= 1 CPI
If average CPI for Load / Store instruction is increased by 10%, new average CPI New CPI for Load / Store = 2.5 (100 +10)/100
= 2.5 1.1 = 2.75 CPI
Hence, new execution time will be
ExecutionTime(E.T) = (702.75+1101+203)x(1/500106)seconds
= (192.5+110+60)/(5108)seconds
= 362.5 2 10−9 seconds = 725 10−9 seconds
= 725 nanosecondsQ. 2 Solution:
Solution A (0-Address Code)
PUSH B
PUSH C
ADD ; gives B+C PUSH A
MUL ; gives A(B+C) PUSH 2
PUSH A
MUL ; gives 2A PUSH C
MUL ; gives 2AC
PUSH B
DIV ; gives 2AC/B
SUB ; gives A(B+C) - 2AC/B
PUSH C
PUSH C
MUL ; gives C2
ADD ; gives POP D
A(B+C) - 2AC/B + C2Solution A (1-Address Code)
LDA C MULA C STA X
LDA A MULA C MULA 2
; loads the value stored at memory location C in Accumulator ; gives C2
; stores C2 at memory location X
; loads the value stored at memory location A in Accumulator ; gives AC
; gives 2AC
DIVA B ADDA X STA Y
LDA B ADDA C MULA A SUB Y STA D
; gives 2AC/B
; adding 2AC/B with C2 stored in X gives 2AC/B + C2 ; stores 2AC/B + C2 at memory location Y
; loads the value stored at memory location B in Accumulator ; gives (B+C)
; gives A(B+C)
; subtracts 2AC/B + C2 from A(B+C)
; stores the result at memory location D